For those who are unaware, the Facebook company that owns Instagram and WhatsApp just rebranded to ‘Meta‘. This was revealed with a Connect 2021 event where CEO Mark Zuckerberg talked about his plans for the future, including a virtual reality ‘metaverse’ where people can interact with each other over the internet.
This week, Meta’s AI sector posted a blog post about ReSkin, a “versatile, replaceable, low-cost skin for AI research on tactile perception”. They will be conducting research with Carnegie Mellon University and developing this new robot skin that will sense a ‘touch’ input with great precision. This input will then be fed into AI models and will be used for creating convincing virtual surfaces in the future.
Due to the large amount of data needed for research, Meta needs a lot of tactile sensors. This is why ReSkin is relatively inexpensive to make, costing USD 6 (about RM25) for 100 units and even less for larger orders. It’s also about 2-3mm thick, which makes it useful for robot hands or gloves.
How does ReSkin work?
The blog post talks about the functionality of ReSkin in detail, but to put it simply, there is a stretchy and soft material with magnetic particles in it called the elastomer, and whenever pressure is applied to it, the magnetometer will sense a change in the particles.
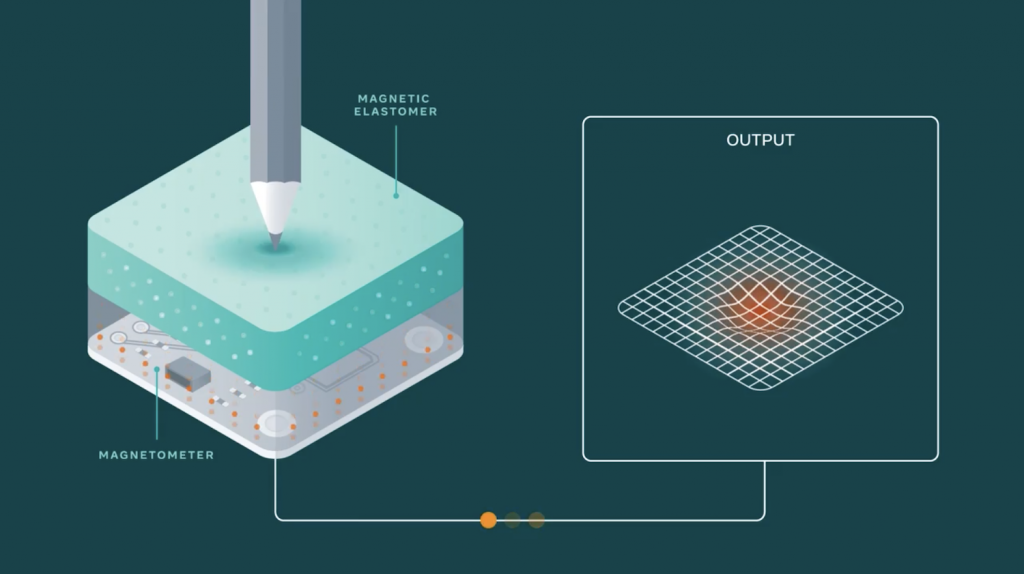
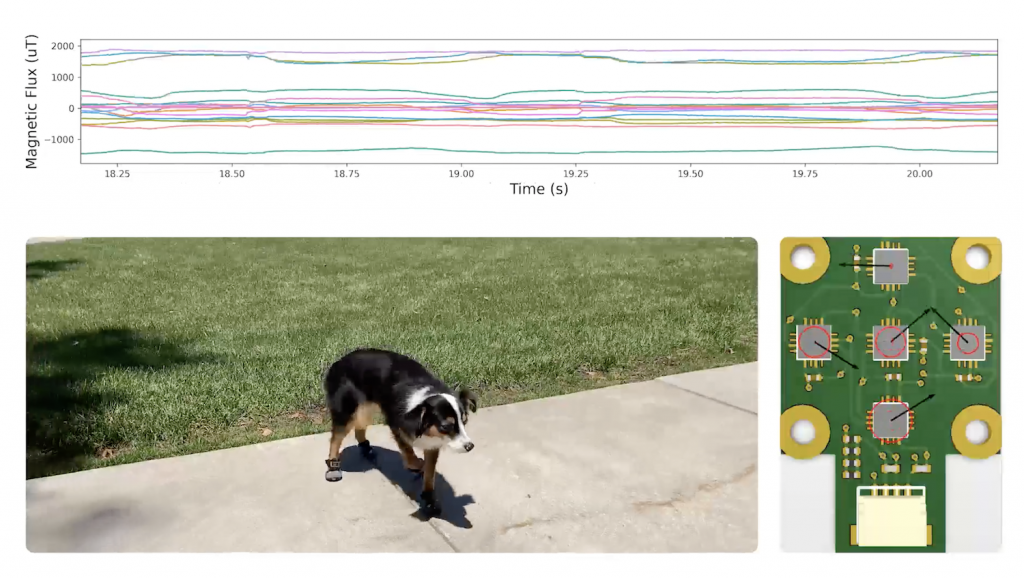
With this simple design, ReSkin can do a lot for robots. It can provide sensitive feedback to robot grippers to prevent them from destroying delicate grapes or blueberries. It can also measure tactile forces from humans and even dogs!
Lerrel Pinto, an assistant professor at NYU mentioned how tactile sensors are a bottleneck in robotics. He then said, “Current sensors are either too expensive, offer poor resolution, or are simply too unwieldy for custom robots. ReSkin has the potential to overcome several of these issues. Its lightweight and small form factor makes it compatible with arbitrary grippers, and I’m excited to further explore applications of this sensor on our lab’s robots.”
So what’s next for ReSkin? Meta hopes that it will help researchers build better AI models with the detailed data. They are also announcing an open source ecosystem for touch processing, releasing free tools like DIGIT, TACTO, and PyTouch.
[ SOURCE, VIA, IMAGE SOURCE ]