Nissan‘s sole official distributor in Malaysia, Edaran Tan Chong Motor, has announced that it will be launching an all-new e-Power hybrid model here in Malaysia by Q4 2024. But unlike hybrid systems of brands such as Toyota and Honda, Nissan’s e-Power works slightly differently.
What is e-Power, and how does it work?
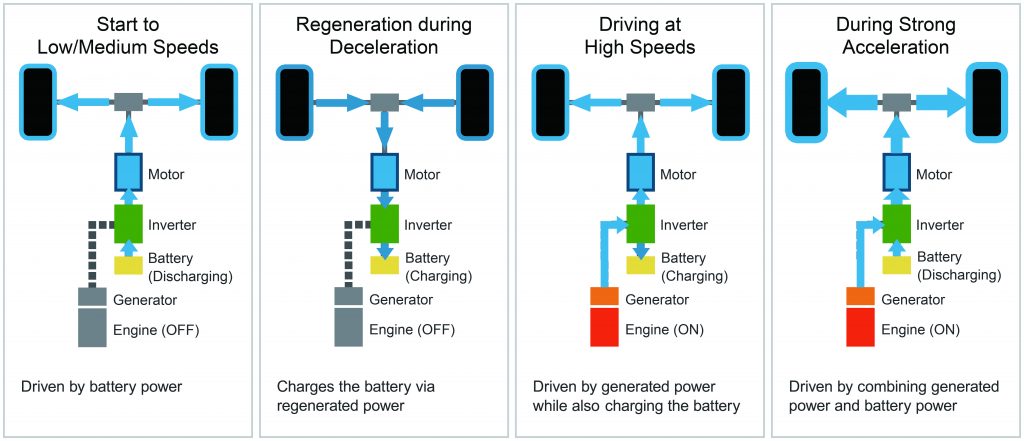
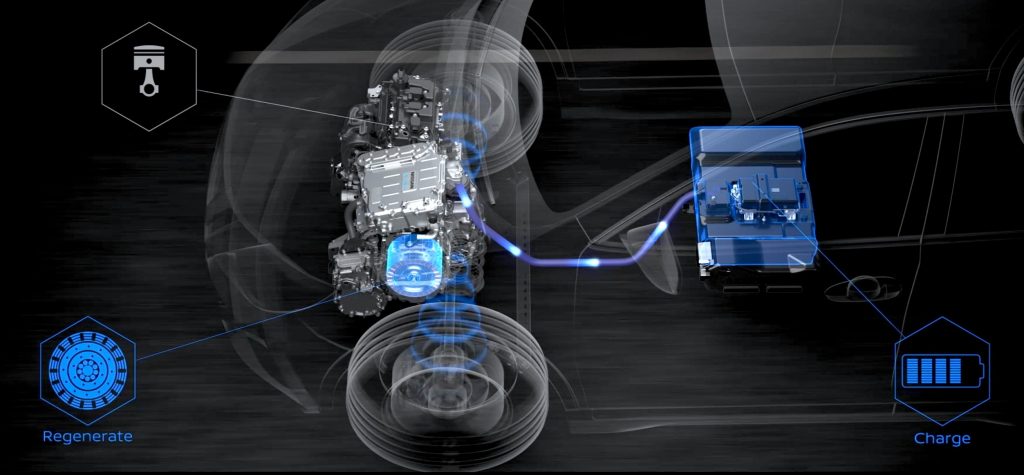
First introduced in 2016, Nissan’s e-Power hybrid system essentially features a petrol gasoline engine and an electric motor. But unlike the traditional hybrid systems most of you might be familiar with, the wheels of an e-Power vehicle are solely powered by the electric motor. The engine on the other hand plays the role of a generator, supplying power to the small lithium-ion hybrid battery pack.
This in theory might sound like how a range-extender EV works. However, the battery pack in a Nissan e-Power vehicle is much smaller in capacity than the ones typically found in a range-extender EV. This results in the engine needing to kick in from time to time to supply power to the battery.
Also, unlike EVs and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs), you can’t externally charge the battery of an e-Power vehicle. The battery gets its sole power source from the petrol engine.
So, how does Nissan’s e-Power system operate in real life? When travelling at low to medium speeds, such as when being driven in urban areas, only the electric motor is needed to power the vehicle. When running at high speeds, the engine will kick in at optimal RPM to power the electric motor. The electric motor will garner energy from both the engine and the lithium-ion battery pack whenever maximum performance is needed.
Nissan has also taken measures to reduce the NVH of its e-Power vehicles. The system’s engine is programmed to only operate on a fixed-point basis where the engine is at its most efficient range to generate electricity.
Additionally, the engine will only come on in phases when the ambient noise is high, such as when cruising on the highway. This is to make sure that the operation of the engine is masked acoustically.
What’s different between Nissan e-Power and other hybrid systems?
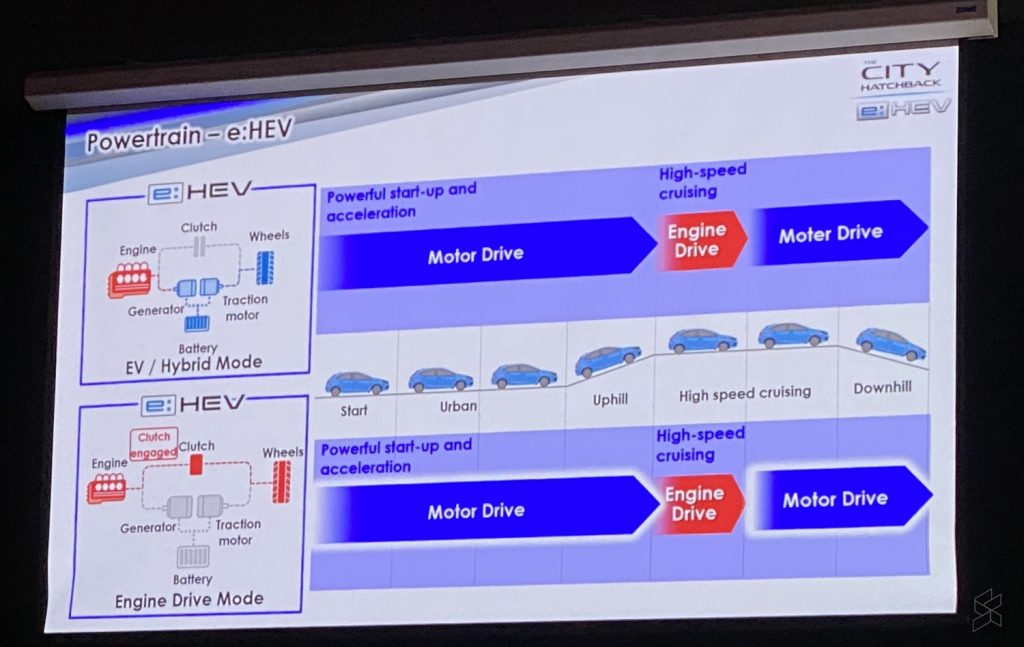
The way Nissan’s e-Power system operates might sound rather similar to Honda’s i-MMD hybrid system. Found in its e:HEV vehicles, the Honda i-MMD system mainly uses its electric motor to power the wheels. However, the petrol engine can also power the wheels directly whenever extra power is needed or when travelling at high speeds.
The Toyota Hybrid Electric System on the other hand only uses the electric motor mostly when travelling at low speeds. The petrol engine will kick in whenever more acceleration power is required, or when cruising on the highway for instance.
When will Nissan launch its first e-Power vehicle in Malaysia?

Nissan has announced its plan to launch an all-new e-POWER model in Malaysia in Q4 2024. However, the carmaker did not reveal which specific model it will be.
Previously at the 2024 Malaysia Autoshow, Nissan’s sole official distributor in Malaysia, Edaran Tan Chong Motor, showcased an outgoing generation Nissan Kicks e-Power wrapped in camouflage. There are also rumours that the sixth-generation Nissan Serena e-Power will be making its way to Malaysia.
The Nissan Kicks e-Power features a 1.2-litre three-cylinder petrol gasoline engine, a front-mounted electric motor which powers the front wheels, and a 1.57kWh lithium-ion battery. This results in a system output of 129hp and 260Nm.
The Nissan Serena e-Power on the other hand sports a 1.4-litre inline-three engine, a front-mounted electric motor which drives the front wheels, and a 1.77kWh battery. Its system output is rated at 163hp and 315Nm.







