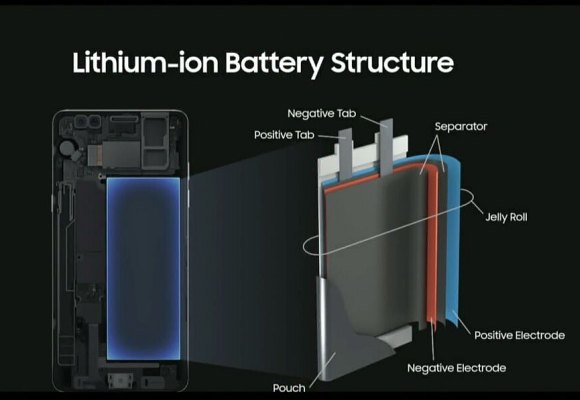
The root cause of the ill-fated Galaxy Note7 problems is finally revealed. After months of internal and independent investigations involving 700 researchers and more than 30,000 batteries, Samsung has officially announced their findings and their upcoming measures to prevent such incidents from happening.
Was it due to fast charging, USB Type-C or design? Read on to find out.
What caused the problem?
Samsung had sold about 3 million Galaxy Note7 which 96% of them have been returned worldwide. For the remaining units, Samsung had issued several software updates to gradually reduce its ability to charge to zero. In case you missed it, Samsung had issued two recalls, the first one to replace it with a unit using a new battery and a second recall for a permanent return. To achieve better battery performance, the Galaxy Note7 had a high-density battery that offers 3,500mAh capacity in a much compact size.
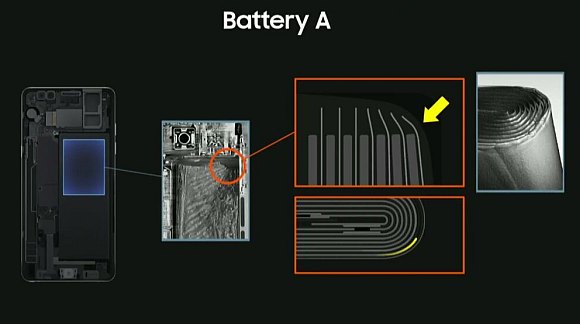
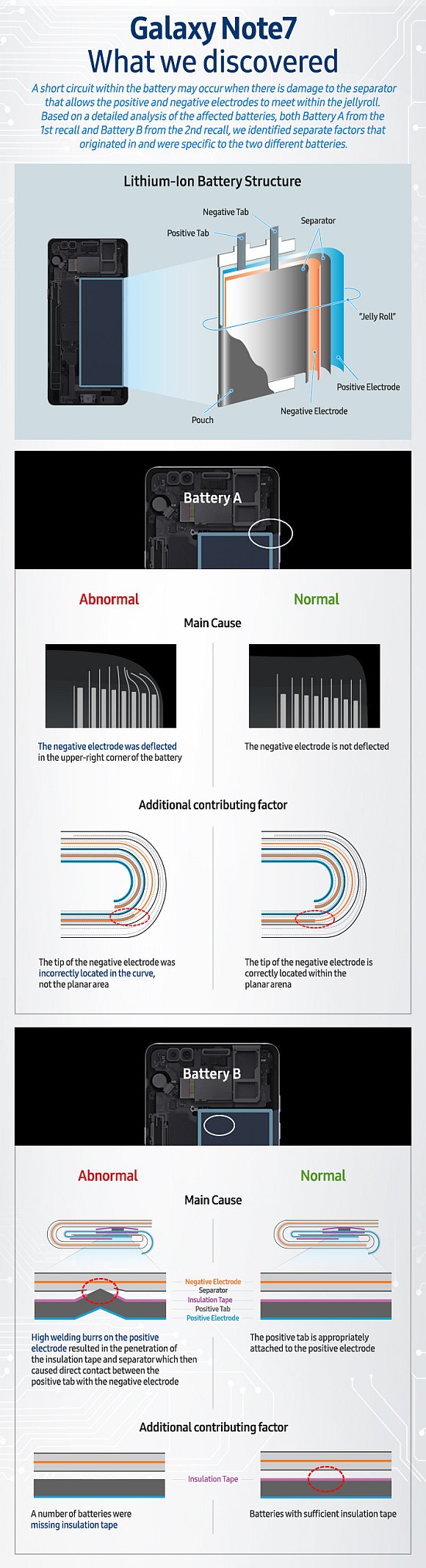
At the press conference, Samsung had invited independent industry groups such as UL, Exponent and TUV Rheinland AG to present their findings of their investigation. In the first Galaxy Note7 battery (Battery A), there’s a deformation at the corner which causes internal short circuit.
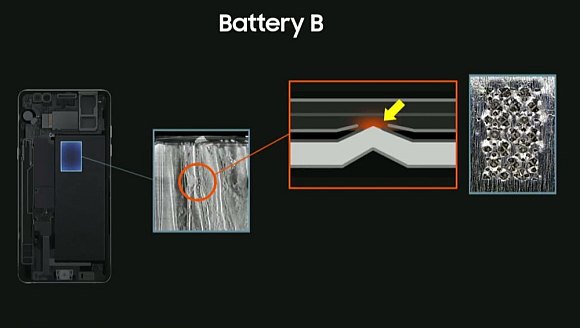
For the second battery (Battery B), there are random protrusions on welding spots which causes internal short circuit. It’s also noted that there’s a lack of insulation tape which increases the risks. According to Sajeev Jesudas, the President of Consumer Business Unit of UL, design and manufacturing issues led to failures of the Galaxy Note7 batteries. According to Kevin White of Exponent, they couldn’t find a fault with the battery system design which takes care of the charging via travel adapter and wireless charging. The Galaxy Note7 came with multiple levels of protection and would prevent any failures from charging.
Samsung’s commitment to safety

Following this incident, Samsung had pledged to be even more committed to product safety. The South Korean company had introduced new internal processes to ensure greater quality and safety for its upcoming models.

On top of that, they had also formed a battery advisory group consisting of external advisers, academic and research experts to ensure the company has a clear and objective perspective on battery safety and innovation.
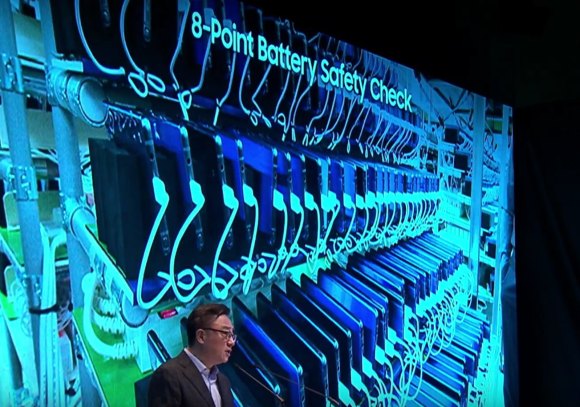
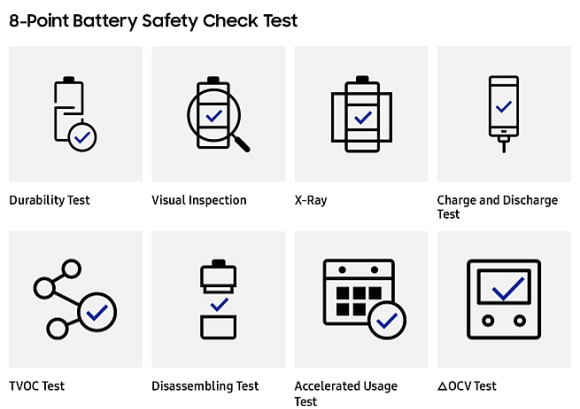
For greater safety assurance, Samsung is also implementing an 8-point battery safety check. This includes durability tests, X-ray scanning, repeated charge and discharge test and disassembly to inspect the quality of its welding and insulation.
At the product planning stage, Samsung has also implemented multi-layer safety measures which include battery safety design, hardware design and an improved software algorithm to manage battery charging temperature, current and duration.
What do you think of these new safety measures? Let us know in the comments below.